 FastAPI-路由2
FastAPI-路由2
# 一、概述
路由方法有 GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE 和 OPTIONS。
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/")
@app.put("/")
@app.delete("/")
@app.get("/")
@app.options("/")
@app.head("/")
@app.patch("/")
@app.trace("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello 454533333343433World"}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 二、路由Route上参数获取和校验
一般我们的路由分会静态和动态,静态路由就是参数是固定写死,也就是访问地址是写死的,而动态地址,就是需要动态的生成,类似简书的博文的地址94710ed35b92就是动态,其实和Bottle和Flask一样。
https://www.jianshu.com/p/94710ed35b92
代码如下:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id):
return {"item_id": item_id}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
上述的示例代码中的item_id 就是一个动态的参数,你可以随意传一个进来。
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/ask
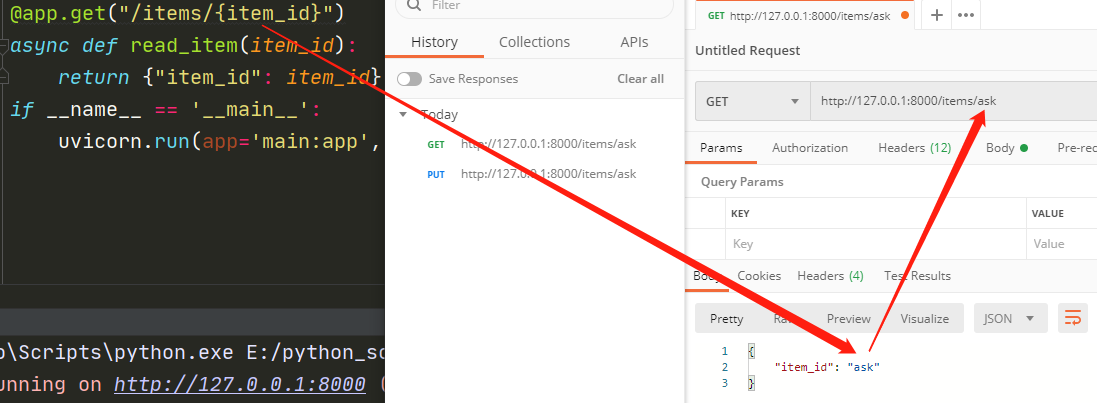
然后就是和bottle(微型Web框架)一样也可以对传入的参数进行数据验证的定义: 如:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: int):
return {"item_id": item_id}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
item_id: int 这种情况item_id必须是可以转为int类似的数据,否则,肯定会报错!
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/ask
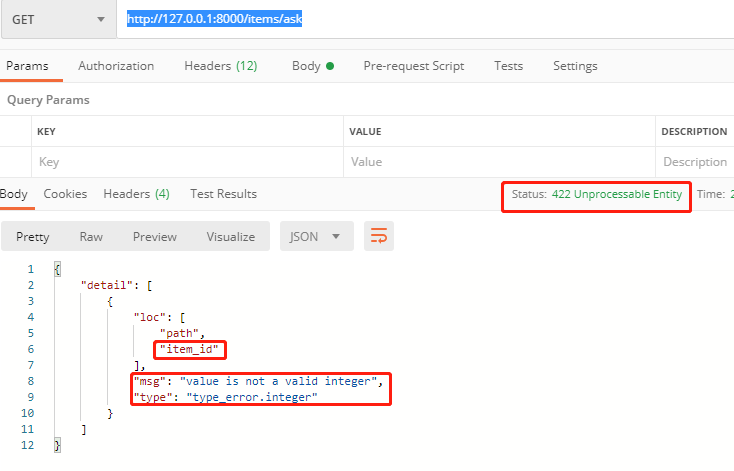
它会给出提示,必须是int类型。返回的HTTP状态码为422
关于路由覆盖问题: 如下两个路由地址:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/users/me")
async def read_user_me():
return {"user_id": "the current user"}
@app.get("/users/{user_id}")
async def read_user(user_id: str):
return {"被优先匹配到:": user_id}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
上面两个路由同时存在的话,会按照匹配规则进行匹配。什么意思呢?
@app.get("/users/me") 表示精确匹配
@app.get("/users/{user_id}") 表示模糊匹配
下面我来验证一下。
http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/me
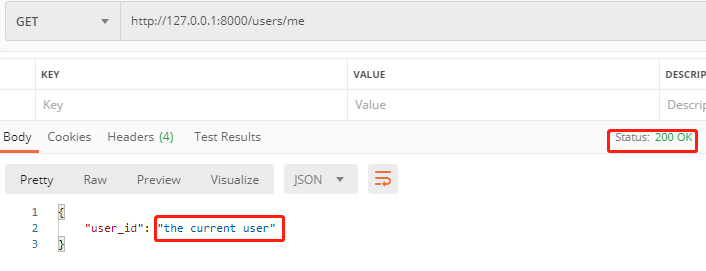
可以看到,它匹配了是第一条。注意:只有正常情况下,才会返回HTTP 200
http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/123
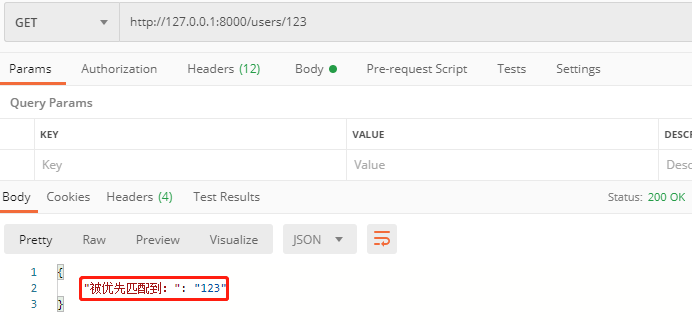
发现它是匹配的第2个路径。
# 查询路径参数和参数校验
关于查询参数,其实就是在使用POSTMAN 提交的时候的参数信息: 如:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=0&limit=10
skip=0&limit 就是所谓的查询参数。
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}]
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_item(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 10):
return fake_items_db[skip: skip + limit]
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 第一种访问的情况:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/
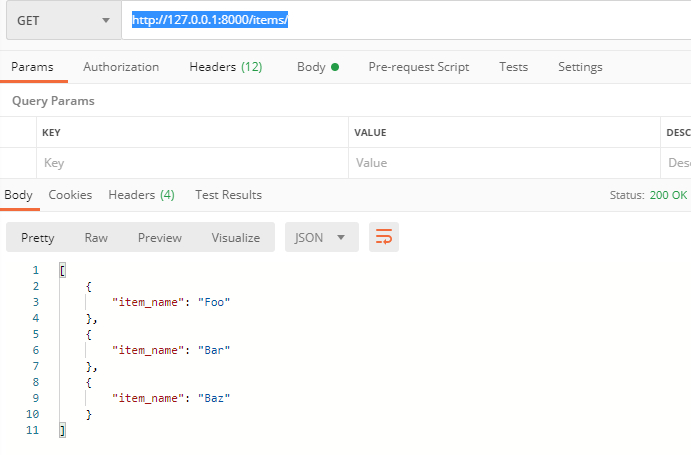
我们发现,它返回的是list所有数据。这是为什么呢?来,我来细细品一下代码。
在这个url中,并没有传入参数skip和limit,那么它会使用默认值,分别是0,100
那么fake_items_db[skip: skip + limit] 等同于fake_items_db[0:10]
看到这里,学过python基础知识的,应该明白,这是列表切片。
# 第二种访问情况:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=1
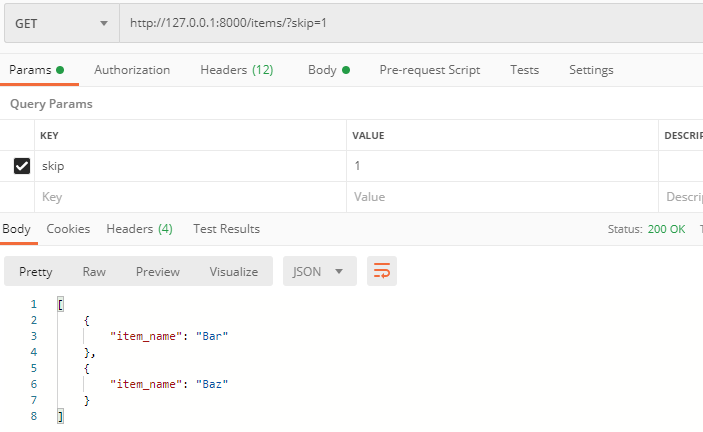
返回了最后2条数据,第一条没有显示。因为此时fake_items_db[skip: skip + limit] 等同于fake_items_db[1:10]
# 第三种访问情况:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=abc
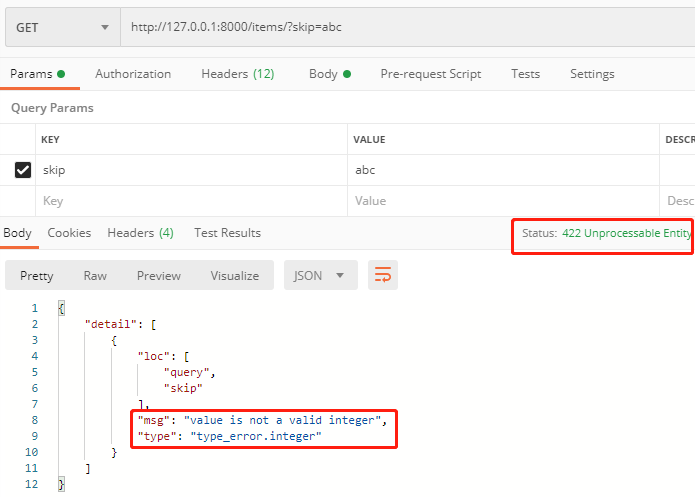
提示错误信息,值不是整形,HTTP状态码为:422
# 多路径和查询参数
所谓的多路径和查询参数就是URL上包含了有动态的参数,还有需要通过&分隔符提交的参数,这情况,通常再GET提交的中也很常见,那么如何处理呐?
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/users/{user_id}/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(
user_id: int, item_id: str, q: str = None, short: bool = False
):
item = {"item_id": item_id, "owner_id": user_id}
if q:
item.update({"q": q})
if not short:
item.update(
{"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"}
)
return item
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
请求:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/123456/items/items_xinxiid/?q=assa&short=True
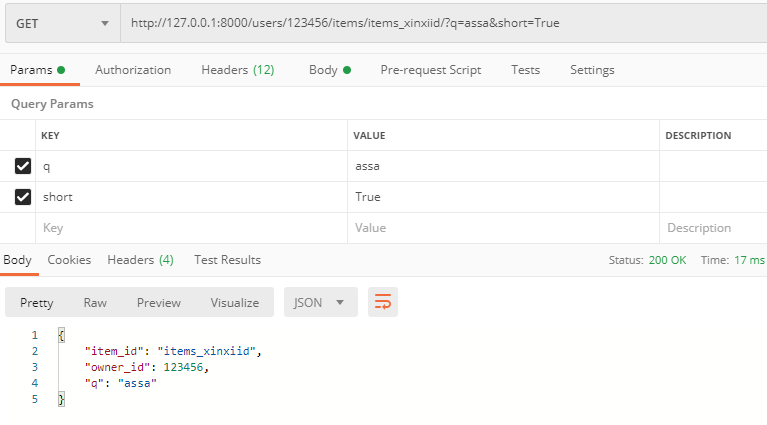
注意:item.update 是python字典的一个语法。存在即更新,不存在,即添加。
其他逻辑我就不解释了,仔细看也能明白。
请求:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/123456/items/items_xinxiid/?q=assa&short=False
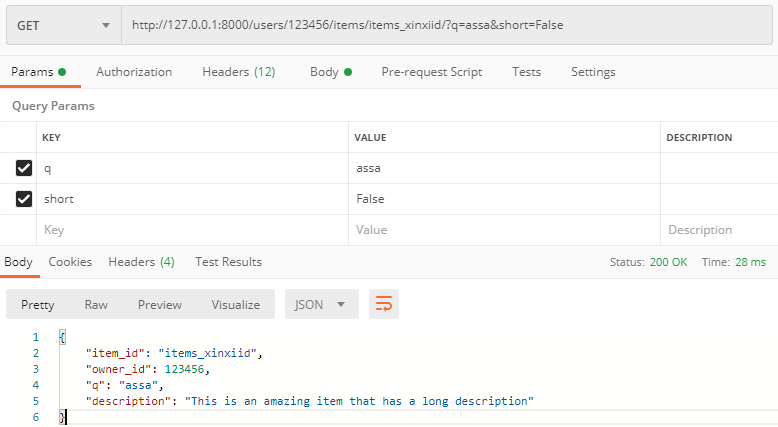
由于short=False,因此description值做了更新操作。
# 路径参数和查询参数的必选和可选
参数的可选和必选主要是通过是否给默认值来决定的,如:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(item_id: str, needy: str):
item = {"item_id": item_id, "needy": needy}
return item
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
上述的代码中 needy 没有给与默认的值,当个没提交这个值的时候,会提示错误:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/123456
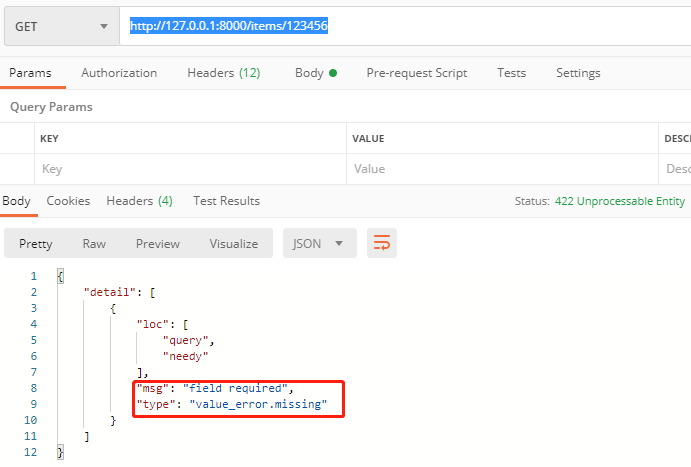
还可以定义可选参数和必选的参数的提交类型: 其中还可以使用Optional来定义需要提交的数据类型: 如:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
from typing import Optional
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(item_id: str, limit: Optional[int] = None):
item = {"item_id": item_id, "limit": limit}
return item
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
我们把查询参数limit规定为了int类型,但是它是可选的的参数,设置为了None:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/ask
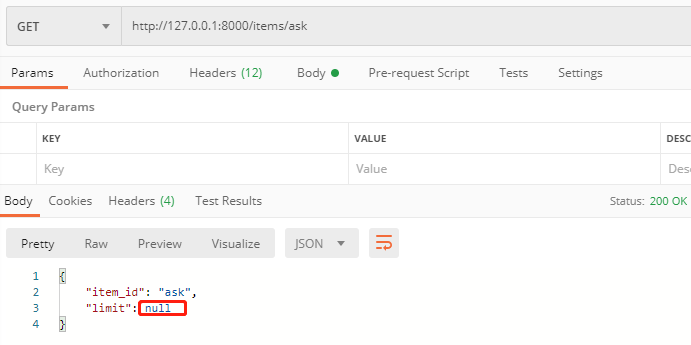
如果传入的参数类型不对,就会报错
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/ask?limit=422w
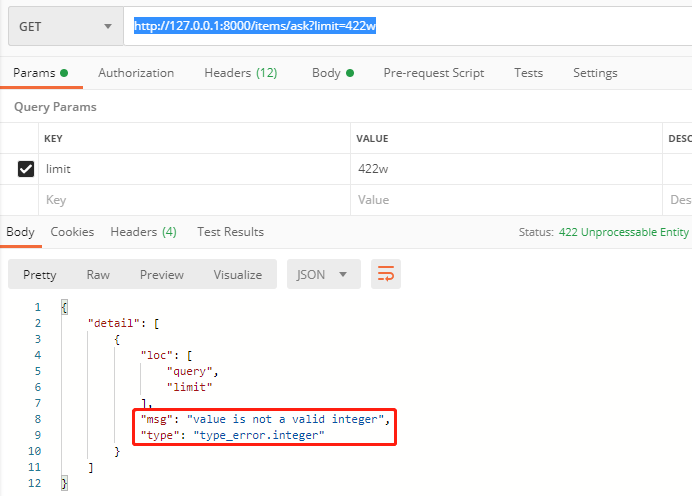
# 路径参数的枚举
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI
from enum import Enum
app = FastAPI()
class ModelName(str, Enum):
alexnet = "alexnet"
resnet = "resnet"
lenet = "lenet"
@app.get("/model/{model_name}")
async def get_model(model_name: ModelName):
if model_name == ModelName.alexnet:
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "Deep Learning FTW!"}
if model_name.value == "lenet":
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "LeCNN all the images"}
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "Have some residuals"}
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
访问地址:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/model/alexnet
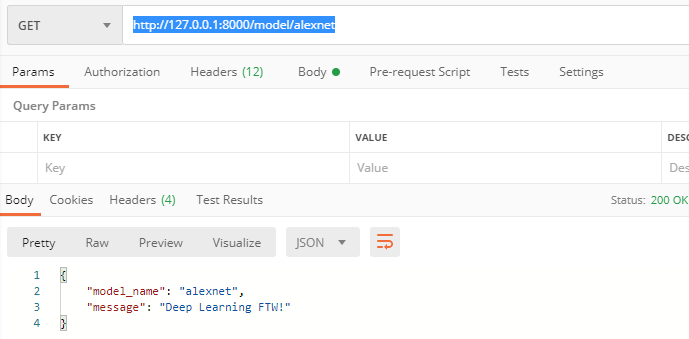
可以发现,它匹配了第一条规则。
# 查询参数Query参数的其他校验
在以前通常是使用wtform来定义提交的字段信息的类似或可选或长度类型。在Fastapi里面,我们是通过: from fastapi import FastAPI, Query 中的Query来定义,如:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str = Query(None, min_length=3,max_length=50,regex="^fixedquery")):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
注意:参考文章中有一个小错误,regex必须在Query里面才能生效。
参数解释:
q: str = Query(None, min_length=3,max_length=50,regex="^fixedquery")
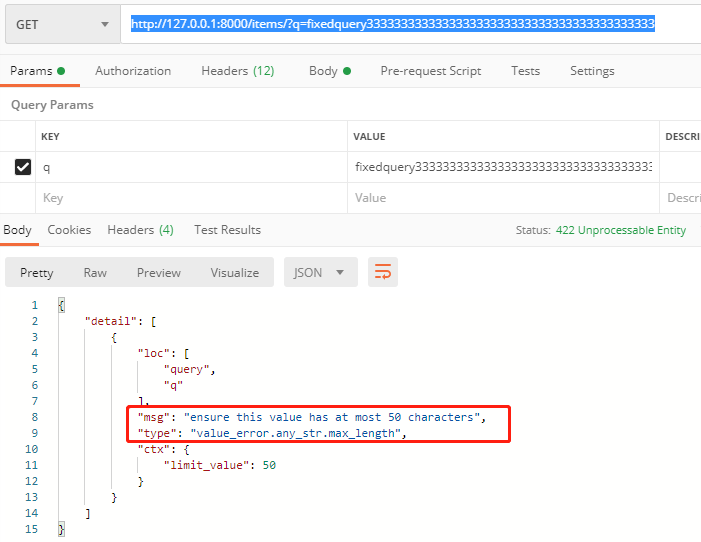
意思是:q参数是可选的参数,但是如果填写的话,最大长度必须是小于50内,且最小的长度
必须大于3: 且需要符合regex的匹配
当然None可以修改为其他默认值,可以写如:
q: q: str = Query('xiaozhong', min_length=3,
max_length=50,regex="^fixedquery"))
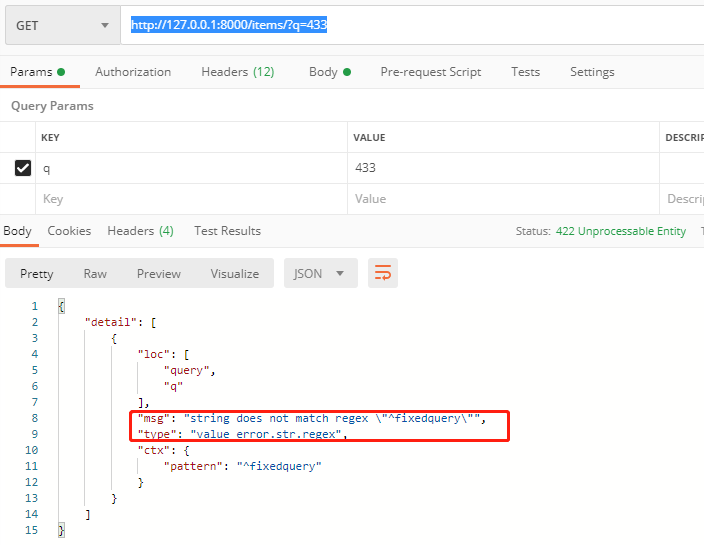
注意:如果正则为^fixedquery$,表示精确匹配,q必须是fixedquery才行。前后左右多一点都不行。
为了下面的测试,我去掉了$
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/
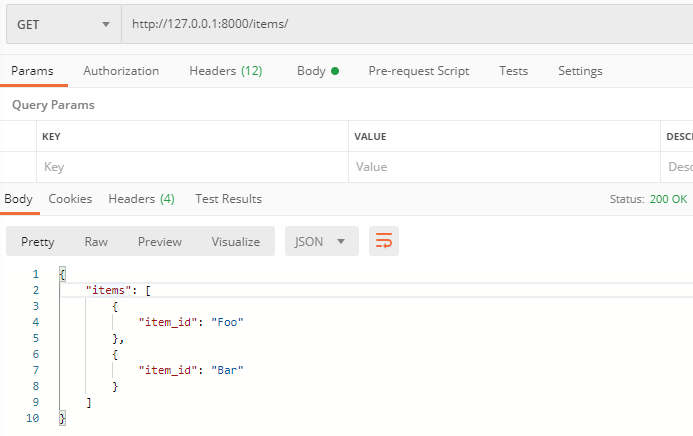
传q的情况下且长度大于50:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=fixedquery333333333333333333333333333333333333333333
传q的情况下且长度小于3:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=fixedquery333
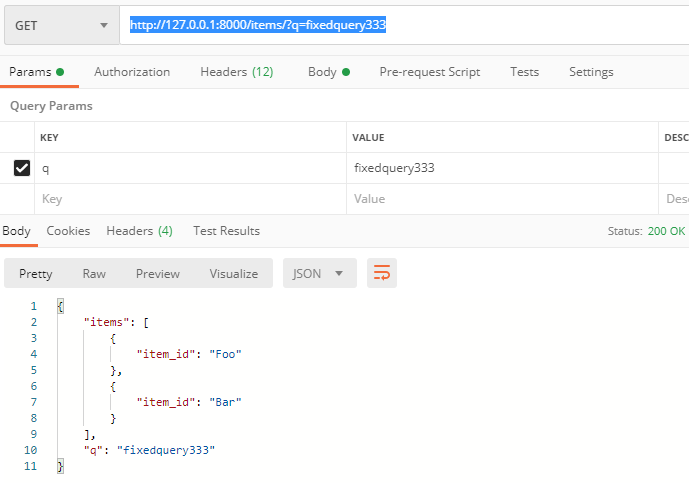
查询参数Query的参数正则校验
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=433
# 查询参数Query参数多值列表
一般在我们的接口中很少说同一个参数提交多个值如:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=foo&q=bar
但也不排查这种情况的存在,所以也可以定义我们的参数类似必须是列表的形式:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing import List
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
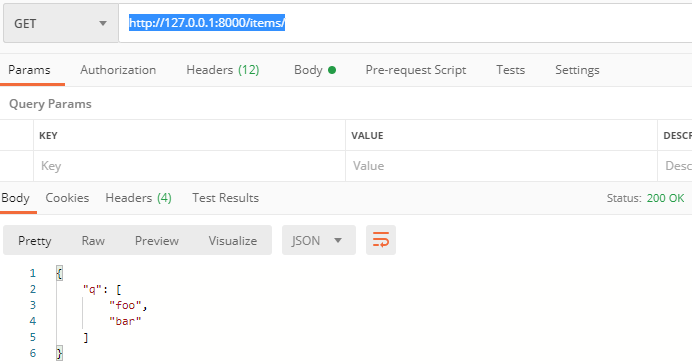
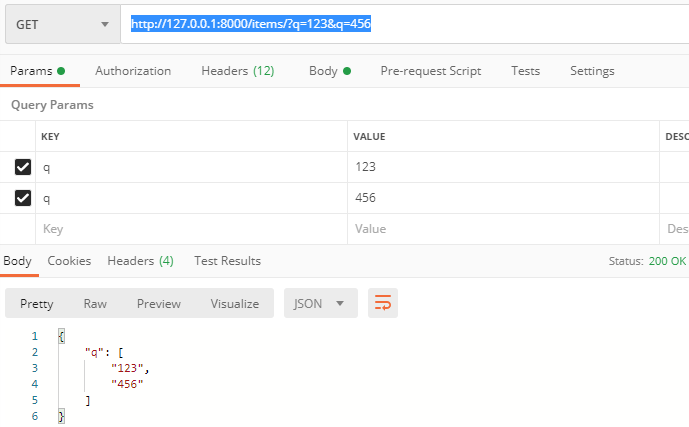
async def read_items(q: List[str] = Query(["foo", "bar"])):
# <!--也可以使用list直接代替List[str]:-->
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
默认值:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/
非默认值:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=123&q=456
# 路径参数的其他校验方式
对于查询参数可以通过Query,同样对于路径参数也可以使用Fastapi自带的Path来进行校验。
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
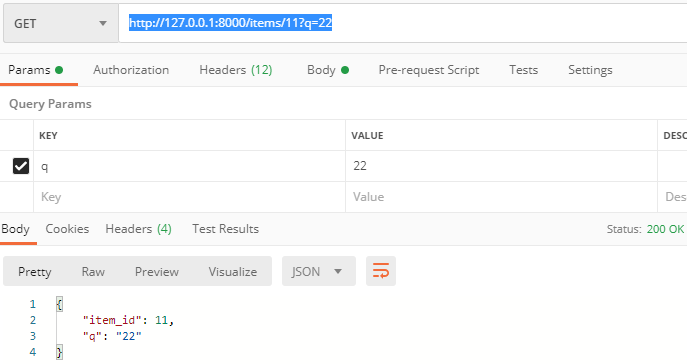
async def read_items(
q: str, item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get")
):
results = {"item_id": item_id}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/11?q=22
对于路径参数校验中,还可以对item_id进行大于或等于的校验如:
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(
*, item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get", ge=1), q: str):
results = {"item_id": item_id}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='main:app', host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True, debug=True)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
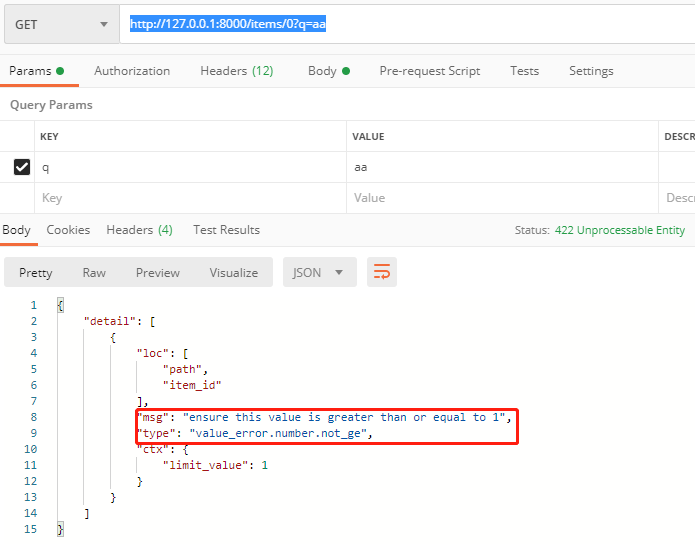
在上面代码意思是,item_id必须是整数,而且必须大于等于1。其中ge=1表示大于等于1
传入0就会报错
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/0?q=aa


 |
|